You may have not listened to the PAL standard. However, it influences your DVD playback: you want to play DVDs from other areas with your DVD player in America, but you find that it cannot work. When you eliminate other causes of the failure, you find that it may be because it uses PAL encoding. Once again you are confused what is the PAL format?
This article will introduce the PAL format clearly to help you know more about this standard.

PAL, the abbreviation for Phase Alternate Line, is a color encoding system for analog television, which is one of the three main standards for color analog television. The PAL format was created in Germany in the late 1950s with the intention of addressing some of the NTSC's shortcomings, such as signal instability in inclement weather, which was particularly important for European broadcasters. In order to eliminate errors, the new standard reverses all other lines in a television transmission. Additionally, PAL supplied the 50 Hz picture frequency that was needed locally. It was used in many European countries.
Is the PAL format still used nowadays? The answer is yes. Since the 1950s, a lot has happened in the world, and the problems that these TV standards were intended to address are no longer relevant. However, the resolutions, timings, and other specifications set forth in these video standards are still utilized in contemporary TV sets and displays. Though some countries have converted or are converting the PAL standard to other standards, many countries and regions still use the PAL format. Blu-rays, DVDs, and a variety of other media are still labeled PAL or NTSC.
NTSC is a video system that uses analog color coding. Color television began to overtake black-and-white television in the 1950s, rendering the earlier technical standard outdated. The various color encoding techniques used by American broadcasting organizations at the time were incompatible with one another. The National Television System Committee introduced a new TV standard, NTSC, in 1953.
So, what are the differences between the PAL format and NTSC?
| PAL | NTSC | |
|---|---|---|
| Video Bandwidth | 5.0 MHz | 4.2 MHz |
| Bandwidth | 7 to 8 MHz | 6 MHz |
| Vertical Frequency | 50 Hz | 60 Hz |
| Horizontal Frequency | 15.625 kHz | 15.734 kHz |
| Sound Carrier | 5.5 MHz | 4.5 MHz |
| Lines/Field | 625/50 | 525/60 |
| Active lines | 480 to 487 | 576 |
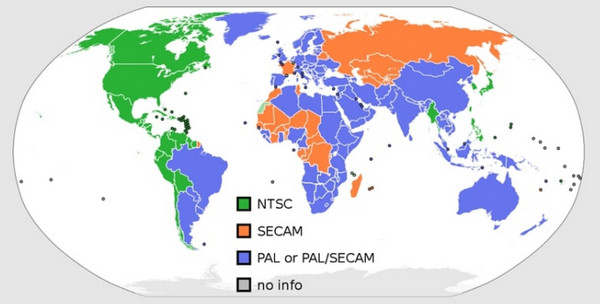
• Distribution area
PAL: Most European countries, most of Asia Pacific, several African countries, Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, etc.
NTSC: Most of the Americas (except Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay), South Korea, Myanmar, Taiwan, Philippines, Japan, and some Pacific Islands nations.
• Color encoding
In order to eliminate hue inaccuracies, the PAL standard uses phase alternation of the color signal to automatically regulate color. PAL systems also eliminate chrominance phase errors.
For color correction, NTSC receivers provide a manual tint control. Therefore, a correction is required if colors are off-hue since the higher saturation of NTSC systems makes them more obvious.
• Picture quality
Because Europe uses a 50-hertz power supply, PAL lines emit at a rate of 50 fields per second or 25 alternating lines. PAL televisions display motion more quickly because they generate 25 frames per second. In addition to having more lines than NTSC, PAL may have fewer frames per second. In contrast to NTSC, which has 525 lines of resolution, PAL television broadcasts have 625. Better picture quality and resolution result from having more lines because they convey more visual information.

PAL DVD is a particular kind of DVD that has been encoded utilizing the PAL standard. In Europe, Asia, and Africa, its main applications are in television transmission and DVD replication. PAL DVDs have different technical specs and viewing features than their NTSC version.
PAL DVDs typically have a resolution of 720 x 576 pixels and a frame rate of 25 frames per second. In order to improve color stability and quality on screens and minimize color errors, this format employs a color encoding technique that alternates the color signal's phase.
To play PAL DVDs, you need a professional PAL DVD player. We want to recommend an excellent PAL DVD player for you to watch in PAL format.
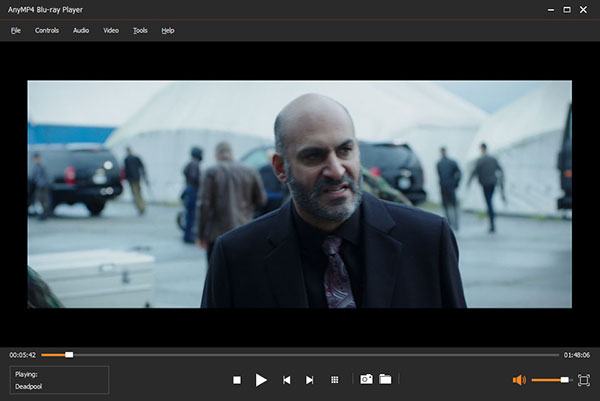
AnyMP4 Blu-ray Player can play PAL format DVDs. PAL DVDs from different regions are encoded with different region codes, such as PAL DVDs from the UK and Germany using Region 2, and PAL DVDs from China using Region 6. This player can rip any region PAL DVD, enabling you to watch any PAL DVD in America, and many other regions. Moreover, it supports playing any DVD type, like DVD-R, DVD+R, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, etc. It adopts Dolby, DTS, DTS-HD, AAC, TrueHD, and surround sound 5.1, and 7.1 channels to provide the superb DVD sound effects. It offers both Windows and Mac versions of computers.
Secure Download
Secure Download
Features
• It provides settings for you to edit video, audio, and subtitle tracks.
• It has the snapshot function to record the highlights of the PAL DVDs.
• You can manage the playback by editing the playlist.
Today, we have introduced you to the full information on the PAL format. After reading this article, you can know its advantages and restrictions in playback. You can use the AnyMP4 Blu-ray Ripper to watch PAL format DVDs freely.
If you have other problems, you can comment on us!